8 Mistakes People Make Buying A Home Battery
By Finn Peacock – Chartered Electrical Engineer, Ex-CSIRO, Founder of SolarQuotes.com.au
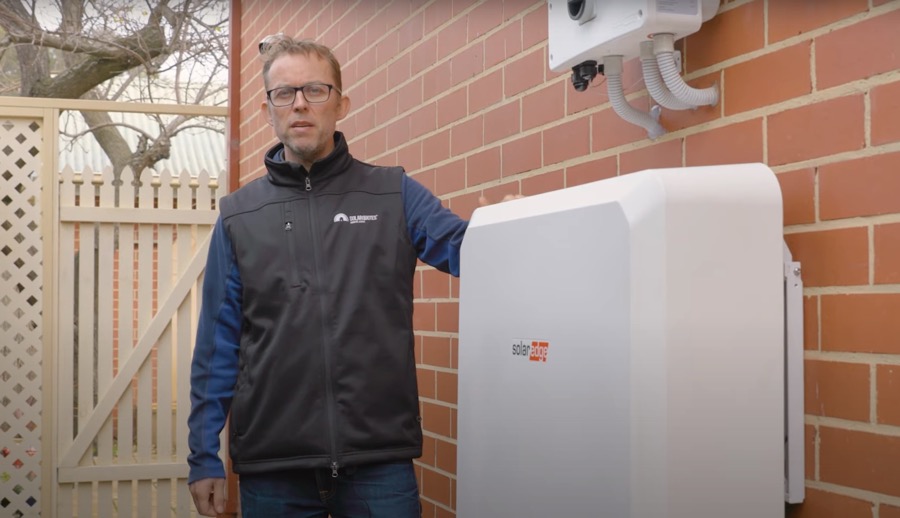

Yours truly with a SolarEdge Home Battery (10 kWh, 5 kW – read on to discover what that actually means…)
Last Updated: 14th May 2025
A well-installed, properly sized home battery can protect you from both blackouts and your electricity retailer.
If the grid goes down, your battery can automatically kick in, keeping your lights and essential appliances running.
If your electricity retailer hikes your tariffs, with a big enough battery and solar, you won’t care.
But home batteries are not cheap. At least the good ones aren’t.
So if you are considering investing in a battery for your home, don’t go in blind.
Here are the biggest mistakes I’ve seen people make when buying batteries. Avoid these, and you’ll be well on your way to getting an excellent system that works trouble-free for many years.
Mistake #1 – Not enough solar
Most people buy batteries primarily to store their excess solar energy. But I see many battery owners with too-small solar systems who don’t have enough excess solar energy to charge their batteries through winter, crippling their battery savings.

I upgraded from 6kW of solar to 20kW!
Most family homes in Australia will need a pretty big solar system to fill a typical home battery throughout the entire year—including winter and overcast days. I’d recommend 10 kW of solar as a minimum, where possible.
Mistake #2 – Buying the cheapest home battery on the internet
It’s not rocket science. Cheap quotes for batteries = low margins for installers = rushed installations with inferior quality products and little-to-no after-sales support.
This is deadly serious. Lithium-ion batteries can store large amounts of energy. When they charge and discharge, they generate heat. If charging and discharging aren’t managed correctly, or there is an electrical fault, “thermal runaway” can occur.
Thermal runaway is a fancy way of saying “big-ass fire”. With the amount of energy stored in lithium batteries, they can burn for hours.
Don’t gamble with your safety to save money on a battery. If you can’t afford a decent battery + installation, don’t buy one at all.
Mistake #3 – Getting ripped off
The only thing worse than paying too little and getting a crap battery is paying too much and getting a crap battery.
It’s depressing how often people are quoted a crazy high price for a small and/or crap battery.
Typically these batteries are promoted by either door-knocking salesman or aggressive letterbox-drop campaigns, with arbitrary end-of-month deadlines pressuring you to sign up fast for a ‘great deal’.
You’d hope overpaying will at least protect you against shoddy installations. Sadly, this isn’t the case. In my experience, many companies that charge sky-high prices for batteries don’t care much for quality installations.
It breaks my heart to field calls from concerned pensioners who have spent a small fortune on a tiny battery sold to them by a doorknocking high-pressure salesman and installed by a clown.
The solution here is – get multiple quotes. You’ll quickly figure out the market rate for a well-installed battery that suits your needs.
Mistake #4 – Only considering a Tesla Powerwall
Tesla makes brilliant batteries. I bought a Powerwall 2 almost a decade ago, and I love it.

Despite the grimace – I really like this battery…
For many years after its release, the Powerwall was, in my opinion, one of the best batteries on the market for a homeowner. It was competitively priced, ‘just worked’, and looked slick.
It was inevitable that competition would arise for such a dominant product. Now, there are heaps of great alternatives to Tesla.
Here’s all the brands I recommend:

Anecdotally, at the time of writing, modular batteries – especially Sungrow and Sigenergy – dominate what I see quoted nationwide.
We keep our battery comparison table updated, so you can see what’s available in Australia and what they cost.
Mistake #5 – Not getting blackout protection
Intuitively, people assume all home batteries will back up your house when the grid goes down.
But I’ve seen plenty of cases where a battery has been installed that won’t back up the home. Or a battery that will provide backup, but won’t recharge from the solar panels until the grid comes back.
Discuss in depth with your installer your expectations for how the battery will perform in the event of grid failure.
Questions to ask your installer:
- How many circuits will it run?
- How many fridges will it start? (Motors in fridges and rainwater pumps etc., will demand around seven times their rated current to get them started.)
- Will the solar charge it up without the grid?
Then – make sure they put that in writing on the quote, so there are no nasty surprises the next time the grid goes down.

My battery-backed-up home during a blackout.
Mistake #6 – Not understanding battery-friendly electricity tariffs and VPPs
Time-of-use Tariffs
Until recent, most people had a ‘flat’ electricity tariff. They paid the same rate for electricity regardless of the time of day.
But ‘time-of-use’ tariffs are rapidly gaining popularity. These charge different rates for electricity depending on the time of day.
Usually, they’ll charge a higher rate in the evening and cheaper rates during the day and after bedtime:
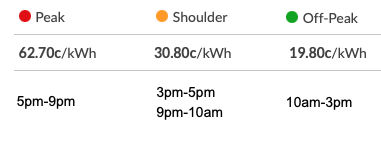
An example Time-Of-Use tariff from South Australia
For a home with solar and a battery, this means you can charge your battery from solar during the day, and usually power through the evening peak on battery power.
Compare the savings for a home in Sydney with a home battery on a flat tariff versus a time-of-use tariff:
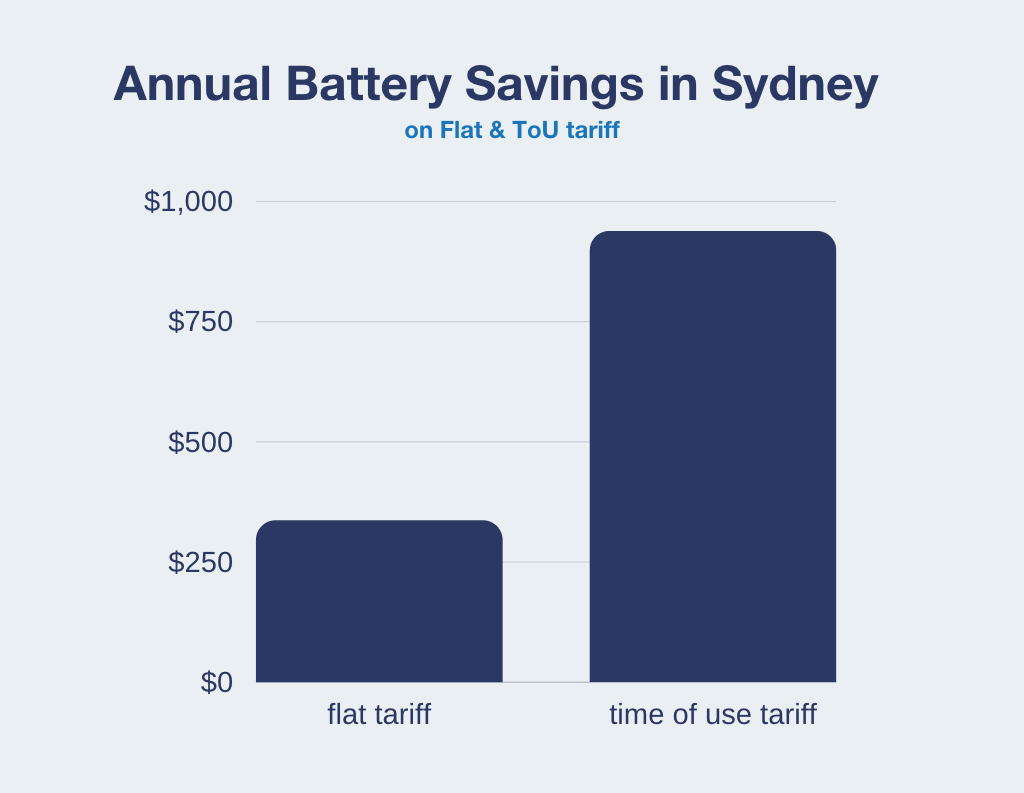
These values are dependent on many variables. See assumptions here.
Virtual Power Plants
Virtual Power Plants (VPPs) are a new kind of tariff for battery owners offered by more and more energy retailers.
If you sign up for one, you give up control of your battery to the VPP operator.
Why would you want to do this? Well:
- You may get an upfront discount on a battery system if you buy a battery through a VPP.
- Some VPPs pay you either a fixed monthly credit, or arrange a profit share from charging or discharging the battery when the grid needs support. Depending on the VPP, this may substantially improve the battery’s economics.
- Some VPPs give you a higher feed-in-tariff and/or lower usage tariffs in return for them controlling your battery.
But there’s no such thing as a free lunch:
- The more you use a battery, the shorter its lifespan.
- Stored energy is usually most valuable in the evening peak. VPP operators may force your battery to charge mid-afternoon (from the grid if there’s not enough solar), discharging into the grid shortly after sundown, leaving you with little or no battery energy to get you through the night.
Make sure you balance the promised savings from joining a VPP with the downsides of giving up control of your battery.
Mistake #7 – Misunderstanding Modular Batteries
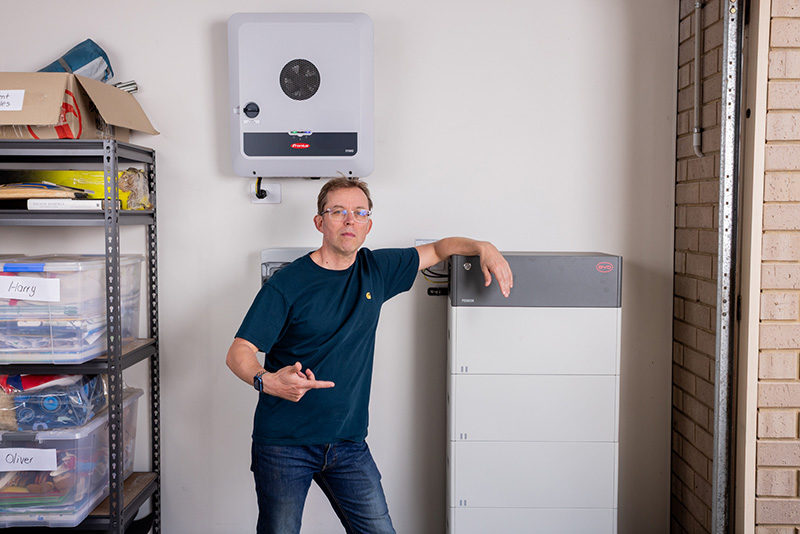

Modular batteries can be expanded by plugging in more modules. Like this BYD B-Box.
I read a well-meaning article recently advising that consumers buy modular batteries. The idea is that you start off with a small battery and then ‘plug and play’ new batteries over the years as your budget allows.
This is a bad idea for a few reasons. Battery models can become obsolete. The odds that you can buy modules for your battery in 2+ years’ time are slim. And expanding your storage capacity so it’s more than specified in the original system design may require other wiring and hardware changes.
From a budget perspective, one of the drawbacks of buying a smaller modular battery is that the required electronics make up a lot of the initial expense. So if you buy a larger unit, you’ll get more ‘battery for your buck’.
For example, if you pay $5000 for a 2.5 kWh unit, $2500 goes toward the battery and $2500 toward the control electronics.
If you buy a 5 kWh unit for $7500, you’re getting 100% more battery for only 50% more money – economies of scale kick in!
Choose and size your battery carefully at the outset – don’t undersize your system thinking you can simply plug and play extra modules later.
Mistake #8 – Not realising Power and Energy are different things
This one is a bit technical. I left it to last to avoid scaring anyone off too soon.
A battery is specified by its Power Input/Output (kW) and Energy Storage Capacity (kWh).
For example, the SolarEdge Home Battery is a 5 kW, 10 kWh battery. It can charge and discharge at a rate (power) of 5 kW and store 10 kWh of energy.
It is essential the battery you buy has enough power and energy storage capacity to meet your needs which may be:
- getting through the evening peak or
- getting through the whole night or
- backing up your whole home
- or something else
…depending on your particular circumstances.
There is a longer explanation of the difference between power and energy here.
The next step
So there you have it – the top mistakes I’ve seen people make when buying a battery.
If you’re considering installing solar and batteries for your home or business, SolarQuotes can help you get quotes from high-quality installers quickly and easily: